线程状态
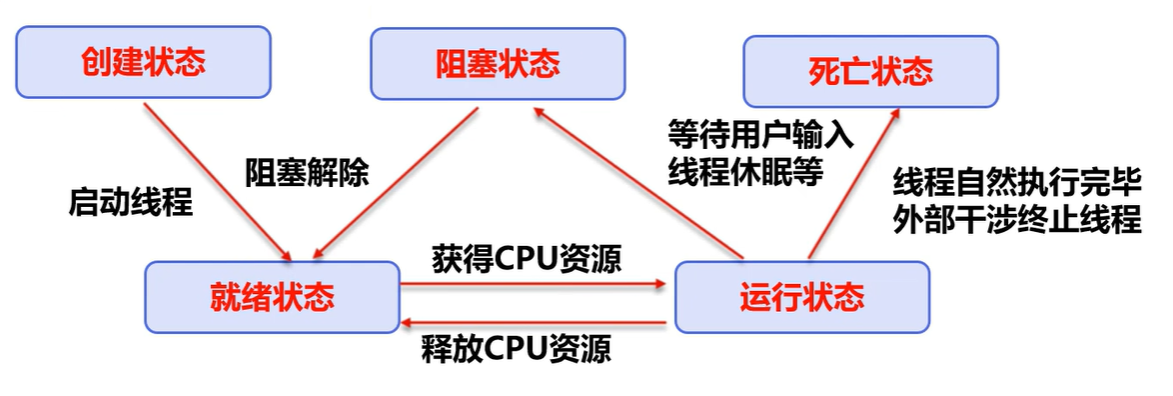
新生状态(new):Thread t = new Thread();
start()->进入就绪状态 但不是立即调度执行
sleep()/wait()/其他同步锁定时 -> 阻塞状态 阻塞解除后,重新进入就绪状态
cpu调度 -> 运行状态
死亡后不可再运行
线程方法
| 方法 |
说明 |
| setPriority(int priority) |
更改线程优先级 |
| static void sleep(long millis) |
使当前线程睡眠 |
| void join() |
(插队)等待该线程终止 |
| static void yield() |
(礼让) 暂停当前正在执行线程,执行其他线程 |
| void interrupt() |
中断线程,一般别用 |
| boolean isAlive() |
测试线程是否处于活动状态 |
线程停止
- 设立标志位来停止线程
- 当flag=false时,线程结束
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| public class TestStop implements Runnable{
private boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 0;
while (flag) {
System.out.println("线程进行中..."+ (i++));
}
}
public void stop() {
this.flag = false;
System.out.println("停停停停停停停停停停停停停停停停停停停停停停停停停停停停");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestStop testStop = new TestStop();
new Thread(testStop).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
if (i == 900000) {
testStop.stop();
}
}
}
}
|
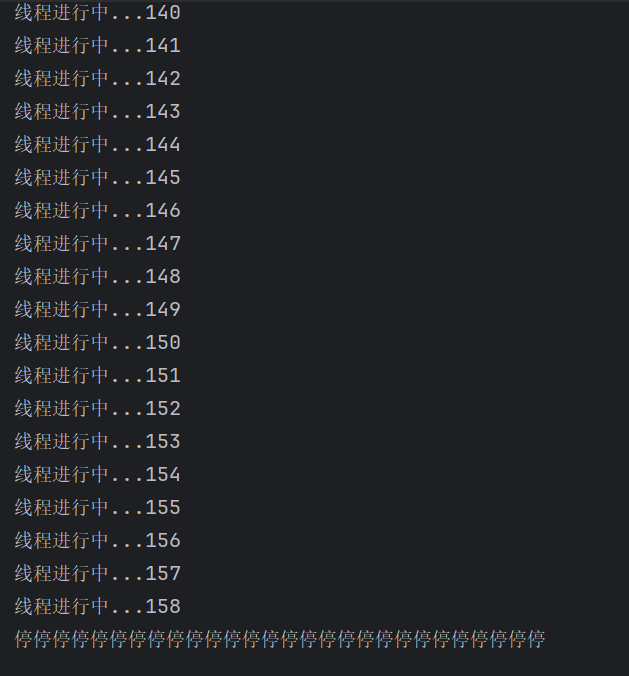
还没到达900000就停止了是因为main线程可能比run线程提前到达900000,所以停止了
线程休眠
- sleep可以模拟网络延时/倒计时
- 每个对象都有一个锁,sleep不会释放锁
模拟网络延时:放大问题发生性(eg.并发问题)
模拟倒计时:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public class TestSleep{
public static void TenSecondsDown() {
int num = 10;
while (true) {
System.out.println(num);
num--;
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
if (num <= 0) {
break;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TenSecondsDown();
}
}
|
线程礼让
- 让正在执行的线程暂停,但不阻塞(运行->就绪)
- 礼让不一定成功,看cpu心情
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public class TestYield {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyYield myYield = new MyYield();
new Thread(myYield,"a").start();
new Thread(myYield,"b").start();
}
}
class MyYield implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程开始执行");
Thread.yield();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程停止执行");
}
}
|

强制执行
join合并线程,待此线程执行完成后,再执行其他线程,其他线程阻塞
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
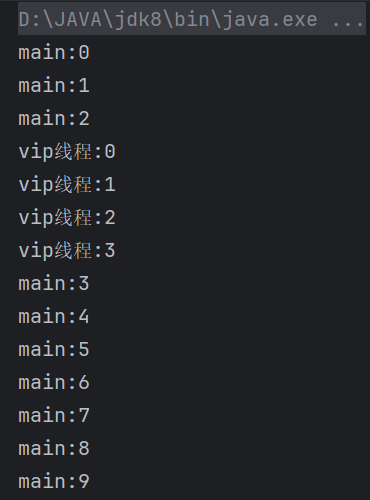
| public class TestJoin implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
System.out.println("vip线程:" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
TestJoin testJoin = new TestJoin();
Thread thread = new Thread(testJoin);
thread.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("main:" + i);
if (i == 2) {
thread.join();
}
}
}
}
|
线程观测状态
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
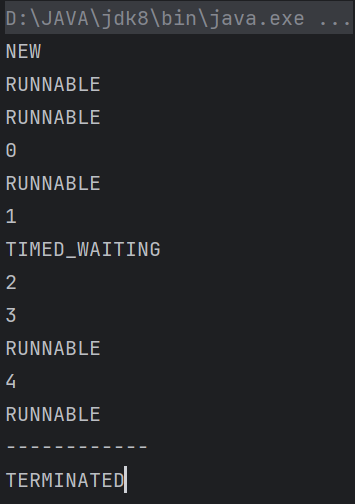
| public class TestWait{
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.println(i);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
System.out.println("------------");
});
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
thread.start();
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
while (state != Thread.State.TERMINATED) {
Thread.sleep(100);
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
}
}
}
|
线程优先级
- getPriority()获取优先级
- setPriority(int xxx)设置优先级
- 优先级的设定一般在start()前
优先级 1-10
优先级低是说明获得调度的概率低
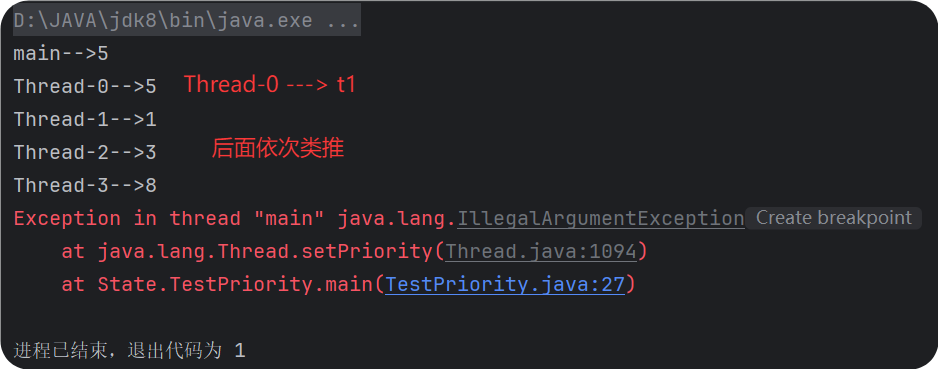
不一定按照优先级顺序运行,要看cpu调度
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| public class TestPriority {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
MyPriority myPriority = new MyPriority();
Thread t1= new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t2 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t3 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t4 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t5 = new Thread(myPriority);
t1.start();
t2.setPriority(1);
t2.start();
t3.setPriority(3);
t3.start();
t4.setPriority(8);
t4.start();
t5.setPriority(11);
t5.start();
}
}
class MyPriority implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
}
}
|
守护(Daemon)线程
用户线程&守护线程
- 虚拟机需要保证用户线程执行完 ->main
- 虚拟机不需要等待守护线程执行完 ->gc
用户线程执行结束后,程序退出,守护线程也会退出(可能有延迟)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| public class TestDaemon {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person();
God god = new God();
Thread thread = new Thread(god);
thread.setDaemon(true);
thread.start();
new Thread(person).start();
}
}
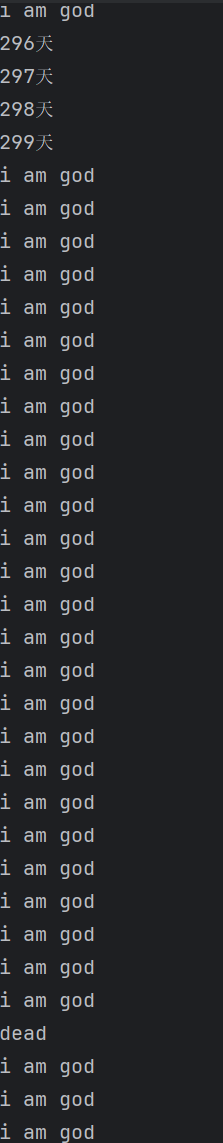
class God implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("i am god");
}
}
}
class Person implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 300; i++) {
System.out.println(i+"天");
}
System.out.println("dead");
}
}
|