反射概述
借助Reflection API取得任何类的内部信息,直接操作任意对象的内部属性和方法
正常方式:引入需要的“包类”名-> new ->取得实例化对象
反射方式:实例化对象 -> getClass()方法 -> 取得“包类”名
通过反射可以视java为动态语言
获得反射对象
- 一个类在内存中只有一个Class对象
- 一个类被加载后,类的整个结构都会被封装在Class对象中
- 通过反射获取类的Class对象,从中获取类的信息
方式
通过对象获得
1
| Class c1 = person.getClass();
|
forname获得
1
| Class c2 = Class.forName("Person");
|
.class获得
1
| Class c3 = Student.class;
|
基本内置类型的包装类都有一个Type属性
1
| Class c4 = Integer.TYPE;
|
int
获得父类类型
1
| Class c5 = c1.getSuperclass();
|
只要元素类型与维度一样,就是同一个Class
下面举例时均与该类有关
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| class Person {
private String name;
public int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public Person() {
this.name = "person";
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
|
获得类的信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Information {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException {
Class c1 = Class.forName("Person");
System.out.println(c1.getName());
System.out.println(c1.getSimpleName());
System.out.println("===================");
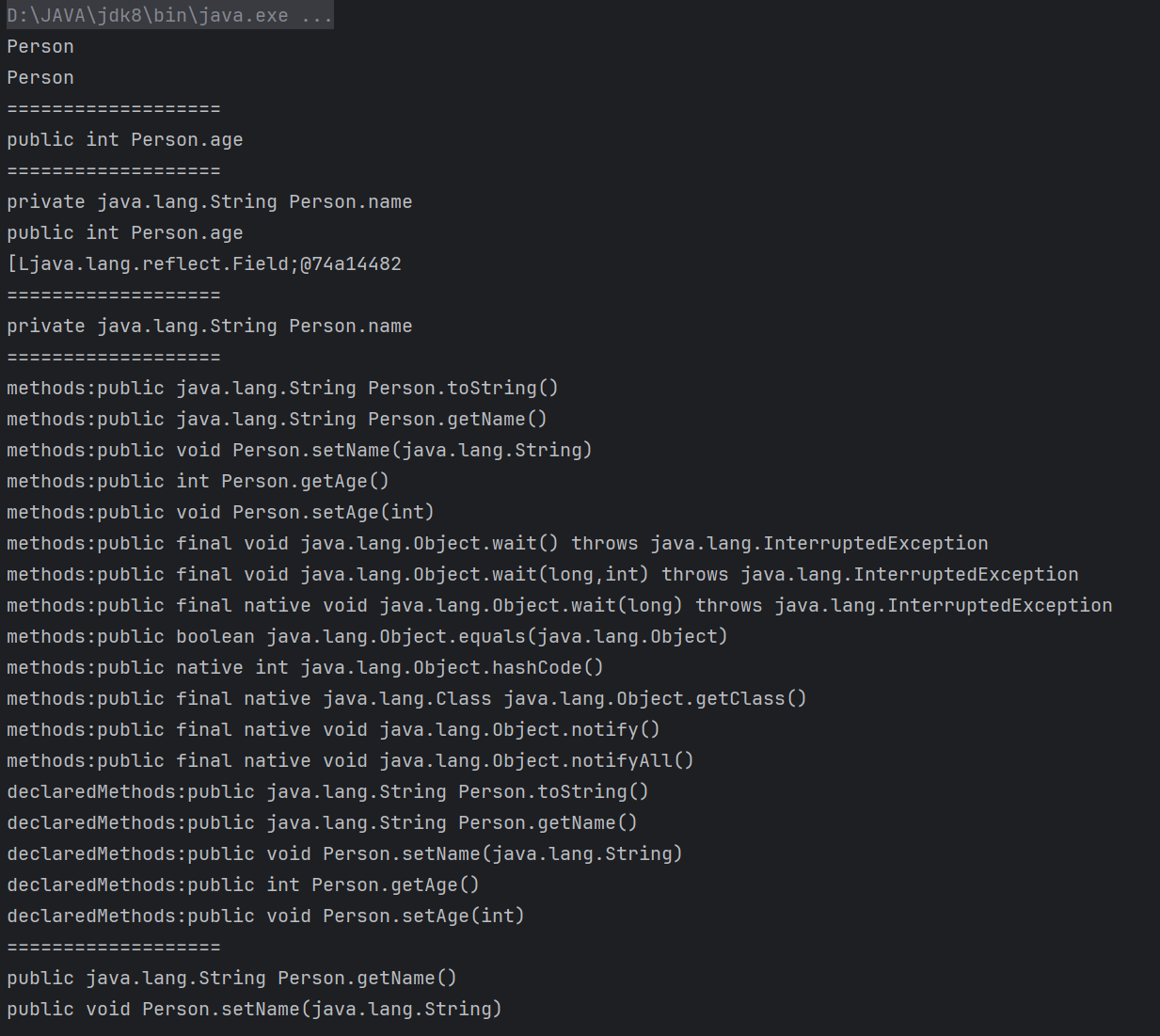
Field[] fields = c1.getFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
System.out.println("===================");
fields = c1.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
System.out.println(fields);
System.out.println("===================");
Field name1 = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
System.out.println(name1);
System.out.println("===================");
Method[] methods = c1.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println("methods:"+method);
}
Method[] declaredMethods = c1.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method declaredMethod : declaredMethods) {
System.out.println("declaredMethods:"+declaredMethod);
}
System.out.println("===================");
Method getName = c1.getMethod("getName");
Method setName = c1.getMethod("setName", String.class);
System.out.println(getName);
System.out.println(setName);
}
}
|
动态创建对象执行方法
创建类的对象
调用newInstance()方法 ->本质调用了无参构造器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class CreateObject {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class c1 = Class.forName("Person");
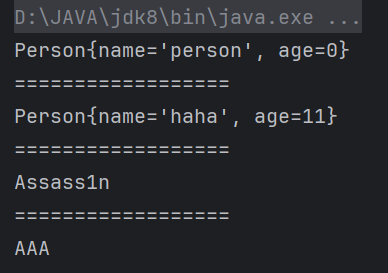
Person person = (Person) c1.newInstance();
System.out.println(person);
System.out.println("==================");
Constructor declaredConstructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class);
Person person2 = (Person) declaredConstructor.newInstance("haha", 11);
System.out.println(person2);
System.out.println("==================");
Method method = c1.getDeclaredMethod("setName", String.class);
method.invoke(person,"Assass1n");
System.out.println(person.getName());
System.out.println("==================");
Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(person,"AAA");
System.out.println(person.getName());
}
}
|
反射操作泛型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| import javax.swing.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class Generic {
public static void Test01(Map<String,Student> map, List<Student> list) {
System.out.println("test01");
}
public Map<String,Student> Test02() {
System.out.println("test02");
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException {
Method method = Generic.class.getDeclaredMethod("Test01", Map.class, List.class);
Type[] genericParameterTypes = method.getGenericParameterTypes();
for (Type genericParameterType : genericParameterTypes) {
System.out.println("#"+genericParameterType);
if(genericParameterType instanceof ParameterizedType){
Type[] actualTypeArguments = ((ParameterizedType) genericParameterType).getActualTypeArguments();
for (Type actualTypeArgument : actualTypeArguments) {
System.out.println(actualTypeArgument);
}
}
}
System.out.println("===================");
Method method1 = Generic.class.getDeclaredMethod("Test02", null);
Type genericReturnType = method1.getGenericReturnType();
if(genericReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType){
Type[] actualTypeArguments = ((ParameterizedType) genericReturnType).getActualTypeArguments();
for (Type actualTypeArgument : actualTypeArguments) {
System.out.println(actualTypeArgument);
}
}
}
}
|
反射操作注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
| import java.lang.annotation.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class TestAnnotation {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class c1 = Class.forName("Student2");
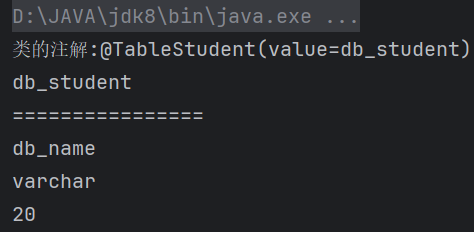
Annotation[] annotations = c1.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println("类的注解:"+annotation);
}
TableStudent tableStudent = (TableStudent)c1.getAnnotation(TableStudent.class);
String value = tableStudent.value();
System.out.println(value);
System.out.println("================");
Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
FieldStudent annotation = name.getAnnotation(FieldStudent.class);
System.out.println(annotation.columnName());
System.out.println(annotation.type());
System.out.println(annotation.length());
}
}
@TableStudent("db_student")
class Student2 {
@FieldStudent(columnName = "db_id",type = "int",length = 10)
private int id;
@FieldStudent(columnName = "db_age",type = "int",length = 10)
private int age;
@FieldStudent(columnName = "db_name",type = "varchar",length = 20)
private String name;
public Student2() {
}
public Student2(int id, int age, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface TableStudent {
String value();
}
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface FieldStudent {
String columnName();
String type();
int length();
}
|